Now that the monitoring system is getting smarter, the monitoring room is getting more and more sophisticated. Party A will come to a high-end, atmospheric, high-grade screen wall composed of more than a dozen splicing screens. There is also an increasing number of surveillance cameras, and the number of DVRs is increasing. It is extremely urgent to configure a good computer room power supply system.
In fact, every one of us who has done a weak electricity monitoring project will face a problem. Party A will always ask a sentence: "Monitoring room power distribution, how much power do you have, how much power do I need to give you?"
Sometimes this is a very aggressive thing, why? The total power can be easily calculated by the device itself, not just an addition. The machine room needs to introduce a large square power cable, but it can't be said for a while.
So it leads to today's theme:
How much current can a single square power line pass? How much power is actually? I know the total power. How much lead-in cable do I need to configure? If the monitoring room is equipped with 2.5 square wires, how much power monitoring system can it bring? In a word: how to use the wire and cable in the construction of the monitoring project.
In fact, this has a professional algorithm, depending on the environment, slightly different. Generally as follows:
The working temperature is 30 °C, and the current carrying capacity under long-term continuous 90% load is as follows:
1.5 square millimeters - 14A,
2.5 square millimeters - 26A,
4 square millimeters - 32A,
6 square millimeters - 47A
16 square millimeters - 92A
25 square millimeters - 120A
Current conversion power:
1A=220W, 10A=2200W, and so on.
If the current carrying capacity is 14A copper wire, that is: 220W × 14 = 3080W, then the 1.5 square copper wire power is 3.08 kilowatts.
Copper core wire allows long-term current
2.5 square millimeters (16A to 25A)
4 square millimeters (25A to 32A)
6 square millimeters (32A to 40A)
Aluminum core wire allows long-term current
2.5 square millimeters (13A to 20A)
4 square millimeters (20A to 25A)
6 square millimeters (25A to 32A)
Actual project description
1. Each computer consumes about 200-300W (about 1~1.5A), so 10 computers need a 2.5mm square copper wire to supply power, otherwise a fire may occur.
2, each splicing screen consumes about 200 ~ 300W (about 1 ~ 1.5A), then 12 computers need a 3 square millimeter copper core wire power supply.
3, each hard disk recorder, matrix power consumption is about 150-200w (about 1A), then 5 hard disk recorders and matrix plus display, counted down also 2 square millimeters of copper power supply.
4, the big 3 air conditioner consumes about 3000W (about 14A), then one air conditioner needs a separate 2.5mm square copper core wire to supply power.
5, in fact, the current ordinary housing line is generally 4 square millimeters of copper wire, therefore, the household appliances that are simultaneously open must not exceed 25A (ie 5,500 watts).
In the fire caused by the power supply, 90% is caused by the joint heat, so all the joints must be welded, and the contact parts that cannot be soldered must be replaced in 5 to 10 years (such as sockets, air switches, etc.).
Long-term current allowed by the national standard
4 square is 25-32A
6 square is 32-40A
In fact, these are theoretical safety values, and the limit values ​​are even larger than these.
The maximum power allowed for a 2,5 square copper wire is: 5500W. 4 square 8000W, 6 square 9000W no problem. The 40A digital meter is absolutely 9000W normal. The 12000W of the machine will not burn.
In fact, there is a current-carrying flow in the copper core wire and cable:
Multiply by 9.5 and multiply by nine.
Thirty-five by three-five, and the two groups are reduced by five.
The conditions have been changed and converted, and the high temperature ninefold copper upgrade.
The number of tubes to be worn is two to three, and eighty-seven percent is full of current.
Brief description:
In this section, the current carrying capacity (safety current) of various insulated wires (rubber and plastic insulated wire) is not directly indicated, but is expressed by "multiplied by a certain number of sections", which is calculated by mental arithmetic.
"Twenty-five times down to nine, go up one minus one" is said to be 2.5mm' and below various cross-section aluminum core insulated wires, the current carrying capacity is about 9 times the number of sections. For example, a 2.5 mm' wire has a current carrying capacity of 2.5 x 9 = 22.5 (A).
The multiple of the current carrying capacity and the number of sections from the wire of 4 mm' and above is lined up along the line number, and the multiple is successively decremented by 1, that is, 4 × 8, 6 × 7, 10 × 6, 16 × 5, 25 × 4. "Thirty-five times by three-five, two pairs of points minus five", said that the 35mm" wire current carrying capacity is 3.5 times the number of sections, that is, 35 × 3.5 = 122.5 (A).
From a wire of 50 mm' and above, the multiple relationship between the current carrying capacity and the number of sections becomes a set of two two wire numbers, and the multiple is successively decreased by 0.5. That is, the current carrying capacity of the 50, 70 mm' wire is three times the number of sections; the 95, 120 mm" wire current carrying capacity is 2.5 times the cross-sectional area, and so on.
"The conditions have been changed and converted, and the high temperature ninefold copper upgrade." The above-mentioned port is determined by the aluminum core insulated wire and the bright coating at an ambient temperature of 25 ° C. If the aluminum core insulated wire is applied in an area where the ambient temperature is higher than 25 °C for a long time, the current carrying capacity of the wire can be calculated according to the above-mentioned calculation method of the mouth and then 10% off; when the copper wire is insulated, the copper core is used. Its current carrying capacity is slightly larger than that of the same specification aluminum wire. The above-mentioned port method can be used to calculate the current carrying capacity of one wire number than the aluminum wire. For example, the current carrying capacity of a 16mm' copper wire can be calculated as a 25mm2 aluminum wire.
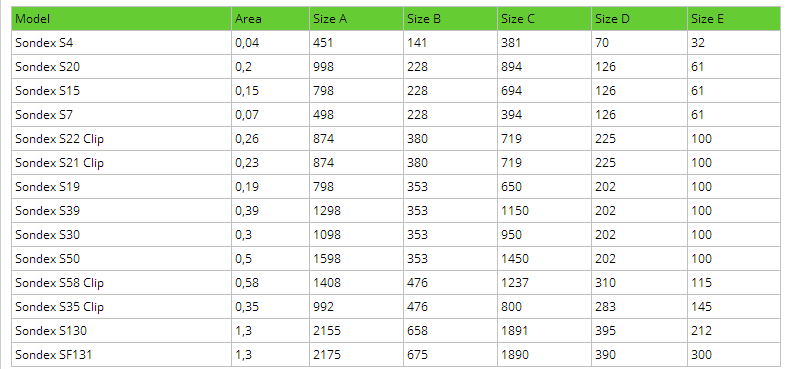
Plate Heat Exchanger Gaskets & Plates for Sondex Products
LIAN JIU Company is a stocking distributor of Plate Heat Exchanger Gaskets, Plate And Frame Heat Exchangers or for Plates for Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers. We also engineer, thermal rate, expand, clean, and sell plate and frame heat exchangers. We have been stocking and selling plate heat exchanger gaskets and heat exchangers for nearly 15 years.
All sizes shown below are in millimeters for use on the chart to the right.
Contact us for any aspect related to gaskets or plate and frame heat exchangers, as well as modifications or new equipment
