Heat Pump In A House,Heating Air Source Heat Pump,Air To Water Heating,Heat Pump Hybrid Water Heater,Heat Pump Home Heating GUANGZHOU GENT NEW ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD , https://www.gentgz.com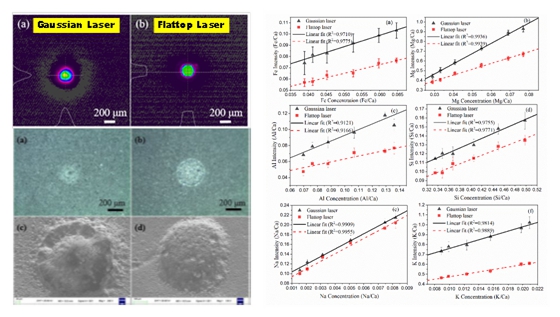
[ Instrument Network Instrument Research and Development ] Recently, Zhang Zhirong's research group, Jia Junwei, used laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) to achieve qualitative and quantitative detection of major trace elements in cement clinker. The related results are published online in the journal Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, entitled "Analysis of element content in cement by Gaussian and flattop laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy". on. This work is of great significance for improving the detection performance of LIBS technology and promoting its practical application.
Detection of main trace elements in cement by LIBS technology
In recent years, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy has become an environmental detection, space exploration, oil and gas mineral resource exploration, agricultural product safety and industry because of its outstanding advantages such as complex sample pretreatment, simultaneous multi-element rapid detection and remote real-time online analysis. Research hotspots in the field of production quality monitoring. However, due to the shortcomings of traditional LIBS technology detection, such as stability and poor sensitivity, it is difficult to apply in practice.
In response to the specific problems of detection stability and sensitivity improvement, the research group used a diffractive optical element (DOE) to convert a Gaussian laser beam whose energy distribution is not uniform in the LIBS system into a flat-topped laser beam with uniform energy distribution, thereby avoiding the sample. Uneven ablation improves the stability and sensitivity of LIBS for the detection of major trace elements in cement. At the same time, using calibration curve and support vector regression method, combined with LIBS technology, quantitative analysis of three cement raw material samples, comparing their concentration range and ability to reduce matrix effect.
The above research work has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences' key projects for foreign cooperation.
(Original title: Anguang's LIBS technology for quantitative analysis of cement composition applications have made new progress)